Backtracking - Word Search
All diagrams presented herein are original creations, meticulously designed to enhance comprehension and recall. Crafting these aids required considerable effort, and I kindly request attribution if this content is reused elsewhere.
Difficulty : Easy
DFS, Backtracking
Problem
Given an m x n grid of characters board and a string word, return true if word exists in the grid.
The word can be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once.
Example 1:
1
2
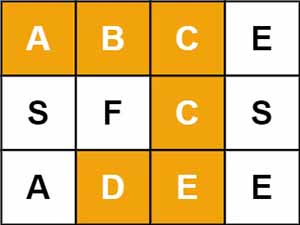
Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED"
Output: true
Example 2:
1
2
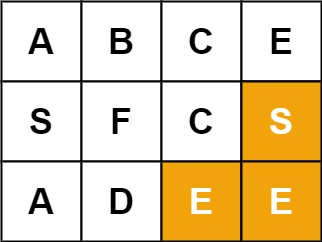
Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "SEE"
Output: true
Example 3:
1
2
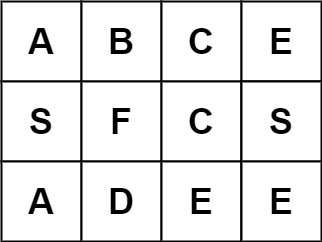
Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCB"
Output: false
Solution
Classic backtracking algorithm where we need to run dfs() from every cell of the board. Start by defining the variables.
1
2
ROWS, COLS = len(board), len(board[0])
path_visited = set()
The dfs() will take the row , col and current index in the word is searching for. As stated, need to invoke dfs() from every cell. If any one of the dfs() returns True then return True, otherwise return False.
1
2
3
4
5
for row in range(ROWS):
for col in range(COLS):
if dfs(row, col, 0):
return True
return False
Now define the dfs() function. If the index reaches the end of the word we have found the word. This is our base/terminating condition, so return True
1
2
3
def dfs(row, col, char_index):
if char_index == len(word):
return True
Otherwise, make sure the cell is,
- not outside of the boundary conditions and
- not visited and
- The char at current
indexmatches with current char in the cell.
Otherwise return False since this indicates its not end of the word yet and there is no possible solution in this path to explore.
1
2
if row < 0 or col < 0 or row == ROWS or col == COLS or (row,col) in path_visited or word[char_index]!=board[row][col]:
return False
Add the location to path_visited .
1
path_visited.add((row, col))
Now run the dfs() for all the four directions. We need to return the True if any of the dfs() returns True
1
found = dfs(row+1,col,char_index+1) or dfs(row-1,col,char_index+1) or dfs(row,col+1,char_index+1) or dfs(row,col-1,char_index+1)
Now perform the backtracking and return found
1
2
path_visited.remove((row, col))
return found
If no solution found, return False.
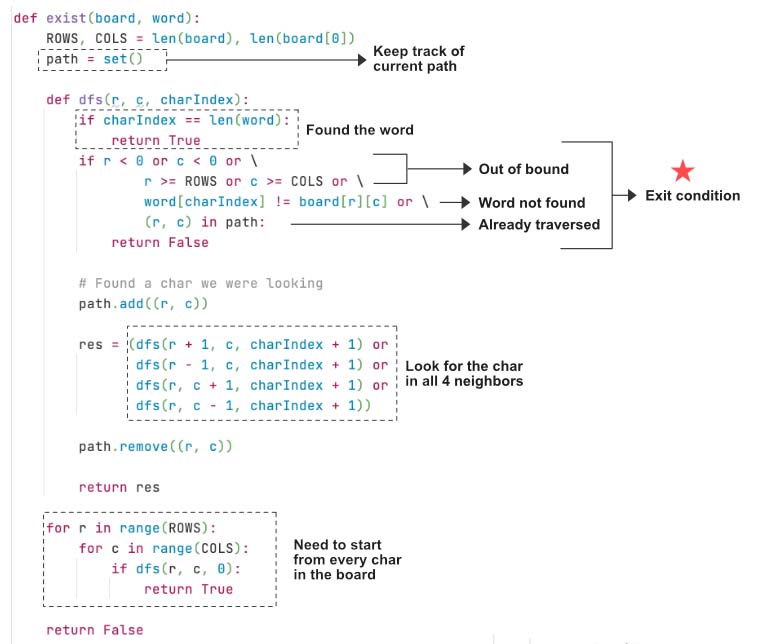
Visualize the code below.
Final Code
Here is the full code.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
def word_search(board, word):
ROWS, COLS = len(board), len(board[0])
path_visited = set()
def dfs(row, col, char_index):
if char_index == len(word):
return True
if row < 0 or col < 0 or row == ROWS or col == COLS or (row, col) in path_visited or word[char_index] != board[row][col]:
return False
path_visited.add((row, col))
found = dfs(row+1, col, char_index+1) or dfs(row-1, col, char_index +
1) or dfs(row, col+1, char_index+1) or dfs(row, col-1, char_index+1)
path_visited.remove((row, col))
return found
for row in range(ROWS):
for col in range(COLS):
if dfs(row, col, 0):
return True
return False