Dynamic Programming - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Cooldown
All diagrams presented herein are original creations, meticulously designed to enhance comprehension and recall. Crafting these aids required considerable effort, and I kindly request attribution if this content is reused elsewhere.
Difficulty : Easy
DFS
Problem
You are given an array prices where prices[i] is the price of a given stock on the ith day.
Find the maximum profit you can achieve. You may complete as many transactions as you like (i.e., buy one and sell one share of the stock multiple times) with the following restrictions:
- After you sell your stock, you cannot buy stock on the next day (i.e., cooldown one day).
Note: You may not engage in multiple transactions simultaneously (i.e., you must sell the stock before you buy again).
Example 1:
1
2
3
Input: prices = [1,2,3,0,2]
Output: 3
Explanation: transactions = [buy, sell, cooldown, buy, sell]
Example 2:
1
2
Input: prices = [1]
Output: 0
Solution
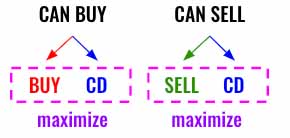
We will be solving this problem using DFS. There are 2 options in each turn.
- If can Buy then Buy or cool down
- If can Sell then Sell or cool down.
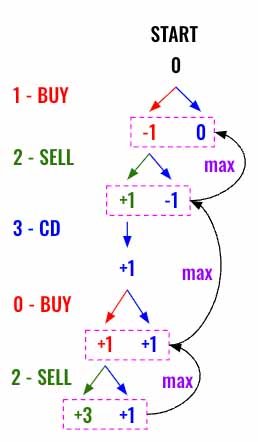
We need to traverse in both the directions, either buy/cool down or sell/cool down and selected which ever provides max profit. Since we are going to use dfs() the max will be starting from leaf nodes at the bottom of the tree and propagate upward.
Here is the visualization for the Example 1. This shows only the partial tree, the max gets propagated from the leaf nodes to the root node.
Lets start by defining our dfs() function. Since the path we can take depends on if we can_buy or not (that is not can_buy means sell) and this is going to be different in each node, let’s pass that to the dfs() function along with the index parameter.
1
def dfs(i, can_buy):
At anytime, if the index i reached the end of the prices then we know we cannot make any more profit, so we return 0.
1
2
3
def dfs(i, can_buy):
if i >= len(prices):
return 0
Now if we are eligible to buy then we can either buy or cool down. Call dfs() by incrementing the index and setting can_buy to False. We also need to subtract the price from returned profit.
1
2
if can_buy:
profit_if_buying_now = dfs(i+1, False) - prices[i]
We also need to traverse the path to cool down instead of buying.
1
profit_if_cooldown =dfs(i+1, True)
Now return the max of both.
1
return max(profit_if_buying_now,profit_if_cooldown)
Alternatively, if we can sell then sell and skip the next element as we need to cool down after selling. Also add the price to profit.
1
2
3
4
else:
profit_if_selling = dfs (i+2, True) + prices[i]
profit_if_cooldown =dfs(i+1, False)
return max(profit_if_selling,profit_if_cooldown)
Now call the dfs() function.
1
return dfs(0, True)
The above code will work fine, however will get timeout error without memorization/caching. Let’s implement that. The dfs() function takes two arguments, so that simplest approach is to create a map using both arguments as keys.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
cache = {}
def dfs(i, can_buy):
if i >= len(prices):
return 0
if (i, can_buy) in cache:
return cache[(i, can_buy)]
if can_buy:
profit_if_buying_now = dfs(i+1, False) - prices[i]
profit_if_cooldown =dfs(i+1, True)
cache[(i, can_buy)] = max(profit_if_buying_now,profit_if_cooldown)
else:
profit_if_selling = dfs (i+2, True) + prices[i]
profit_if_cooldown =dfs(i+1, False)
cache[(i, can_buy)] = max(profit_if_selling,profit_if_cooldown)
return cache[(i, can_buy)]
Final Code
Here is the full code.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
def maxProfit(prices: List[int]) -> int:
cache = {}
def dfs(i, can_buy):
if i >= len(prices):
return 0
if (i, can_buy) in cache:
return cache[(i, can_buy)]
if can_buy:
profit_if_buying_now = dfs(i+1, False) - prices[i]
profit_if_cooldown =dfs(i+1, True)
cache[(i, can_buy)] = max(profit_if_buying_now,profit_if_cooldown)
else:
profit_if_selling = dfs (i+2, True) + prices[i]
profit_if_cooldown =dfs(i+1, False)
cache[(i, can_buy)] = max(profit_if_selling,profit_if_cooldown)
return cache[(i, can_buy)]
return dfs(0, True)