Backtracking - House Robber III
All diagrams presented herein are original creations, meticulously designed to enhance comprehension and recall. Crafting these aids required considerable effort, and I kindly request attribution if this content is reused elsewhere.
Difficulty : Easy
Post Order DFS
Problem
The thief has found himself a new place for his thievery again. There is only one entrance to this area, called root.
Besides the root, each house has one and only one parent house. After a tour, the smart thief realized that all houses in this place form a binary tree. It will automatically contact the police if two directly-linked houses were broken into on the same night.
Given the root of the binary tree, return the maximum amount of money the thief can rob without alerting the police.
Example 1:
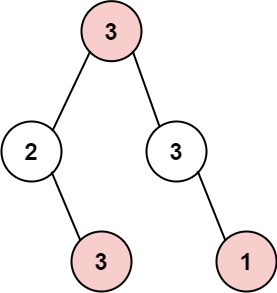
1
2
3
Input: root = [3,2,3,null,3,null,1]
Output: 7
Explanation: Maximum amount of money the thief can rob = 3 + 3 + 1 = 7.
Example 2:
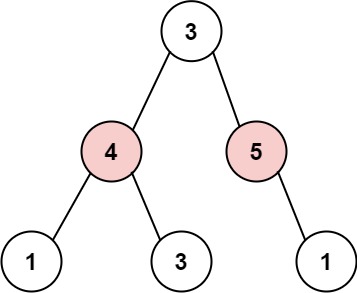
1
2
3
Input: root = [3,4,5,1,3,null,1]
Output: 9
Explanation: Maximum amount of money the thief can rob = 4 + 5 = 9.
Solution
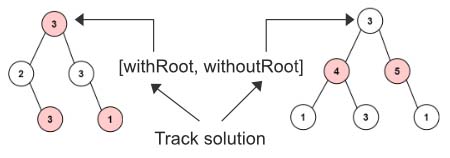
This is one of my favorite problem. Notice the two example given above. The first example uses the root for the best solution and the 2nd one does not use the root for the best solution.
We will be doing the same, always track two solutions for each node.
- Return two solution for each node [
withRoot,withoutRoot] - For every node, perform post-order DFS and find
[withRoot, withoutRoot]. withRoot= Current Node Val + Left Child withoutRoot + Right Child withoutRootwithoutRoot= max(Left Child) + max(Right Child)- Leaf node will have
[0,0]values.
Finally we will return the max([withRoot,withoutRoot])
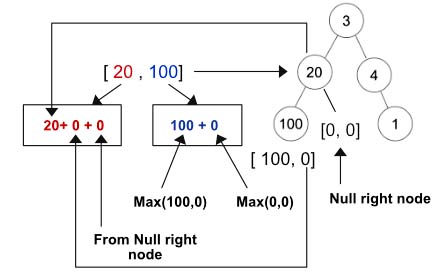
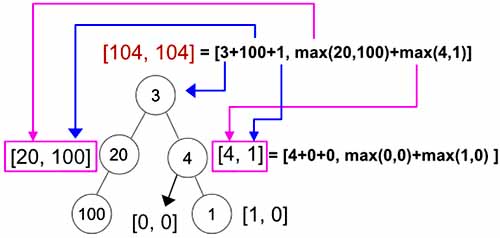
Let’s go through an example first. In the below graph,
- The node
100will return[100,0]. - The node
20’swithRootvalue is20+0+0= 20andwithoutRootvalue ismax(100,0)+max(0,0)=100. It’s going to return[20, 100]
- The node
4at the right will havewithRootas4+0+0=4andwithoutRootasmax(0,0)+max(1,0)= 1. Its going to return[4,1] - Now for the root node, its
withRootvalue is3+100+1=104(Blue Arrow) and itswithoutRootvalue ismax(20,100)+max(4,1)=104 - So finally we return any one of the value as both are same.
Let’s start with the dfs() function. The base/terminating condition is for the leaf nodes. They will have [withRoot, withoutRoot] as [0,0]
1
2
3
def dfs(root):
if not root:
return [0,0]
Now perform traversals in the left and right nodes.
1
2
left_node_val = dfs(root.left)
right_node_val = dfs(root.right)
Calculate the [withRoot, withoutRoot] values for the root node and return.
1
2
3
4
with_root = root.val+left_node_val[1]+right_node_val[1]
without_root = max(left_node_val)+max(right_node_val)
return [with_root,without_root]
Now return the max(dfs(root))
Final Code
Here is the full code.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
def house_robber_iii(root):
def dfs(root):
if not root:
return [0, 0]
left_node_val = dfs(root.left)
right_node_val = dfs(root.right)
with_root = root.val+left_node_val[1]+right_node_val[1]
without_root = max(left_node_val)+max(right_node_val)
return [with_root, without_root]
return max(dfs(root))